散热片一般设计规则
驱动组件内空气的热量可用的体积和温差
接触表面的热界面材料
区和电导率传导和扩散
对流和辐射的面积
表面处理为对流和辐射
在原材料成本最低
最小体积/材料的质量
最低成本的材料
至少在生产过程成本
材料兼容多功能、低成本、低浪费的过程
容易原型、成本有效的大规模生产
强大的机械记忆,安装方便
散热器的设计软件
传热的相关性
快速的信封计算
粗糙的所需散热器的大小
数值设计工具——QFIN
结合相关性和数值传热学计算
更健壮的处理几何细节、流绕过接口、导管、粉丝…
全面的设计工具
Icepak CFD软件,界面为电子冷却
策略+流利的CFD软件——全面能力的工具
选择方法
传热性能:W / oC
鳍密度要求
所需的传播类型
重量和成本:
质量/体积、质量/ W;
成本/体积,成本/ W
形式和形状
鳍方面比率——鳍技术的类型
热传输的距离x,y,和z方向
传播增强
需要热管道吗
散热器的应用
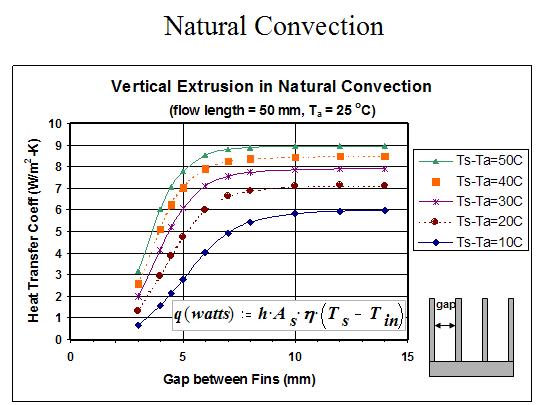
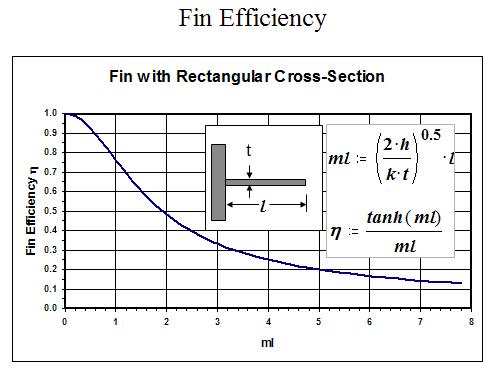
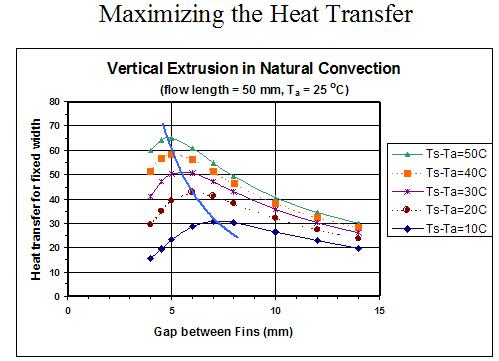
Natural convection
Given heat sink temperature delta above air & length of flow path
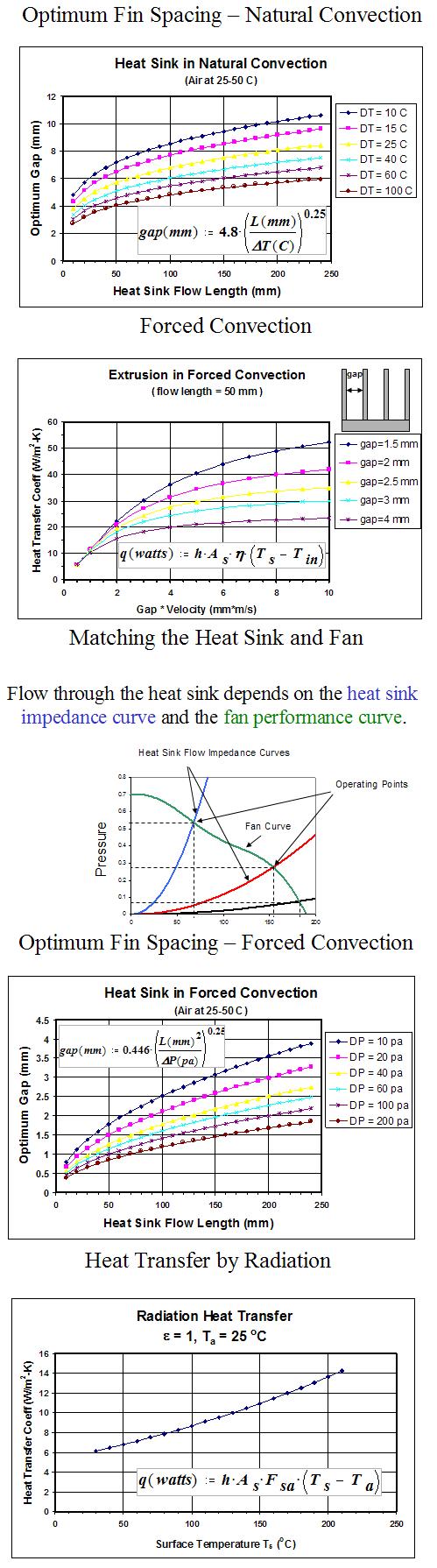
Forced convection
Ducted air flow without bypass
Given fan curve – use limits 0.7*CFM_max & 0.4*P_max
Given max flow and pressure – use pressure for design then check if CFM is within limits
Non-ducted air flow with significant bypass
Use 1.3X dynamic head of approach flow as driving pressure
(will need to solve flow bypass network for final design)
Fan-heat sink
Use 0.5*CFM_max and 0.5*P_max
Mass limits (x,y,z are dimensions in meters)
mass < x*y*((z-0.006)*0.25+0.006)*2700 (kg) – extrusion possible
Otherwise will likely need assembled fin technology heat sink
Fin Density Required
x-y is plane of heat sink base, z is normal to base
Check thermal performance requirement
Separate spreading resistance to get ~fin resistance required
Spreading – from heat source over x-y size & base thickness (Seri Lee Formula)
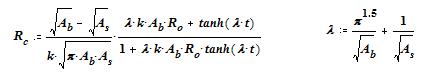
W/oC/cu. in. of Fin Volume – select fin density (Al Fins)
Below 0.03 – Natural Convection possible
Below 0.20 – Low Density Fins, Low DP (gaps >~ 3 mm)
Below 0.40 – High Density Fins, Low DP (<~20 Pa)
Below 0.65 – High Density Fins, High DP (Blowers)
Above 0.80 – Look for liquid or two-phase radiator type HS
If getting close to each limit, consider next higher option or copper
The above performance limits increase by 15% if weight limits allow copper fins.